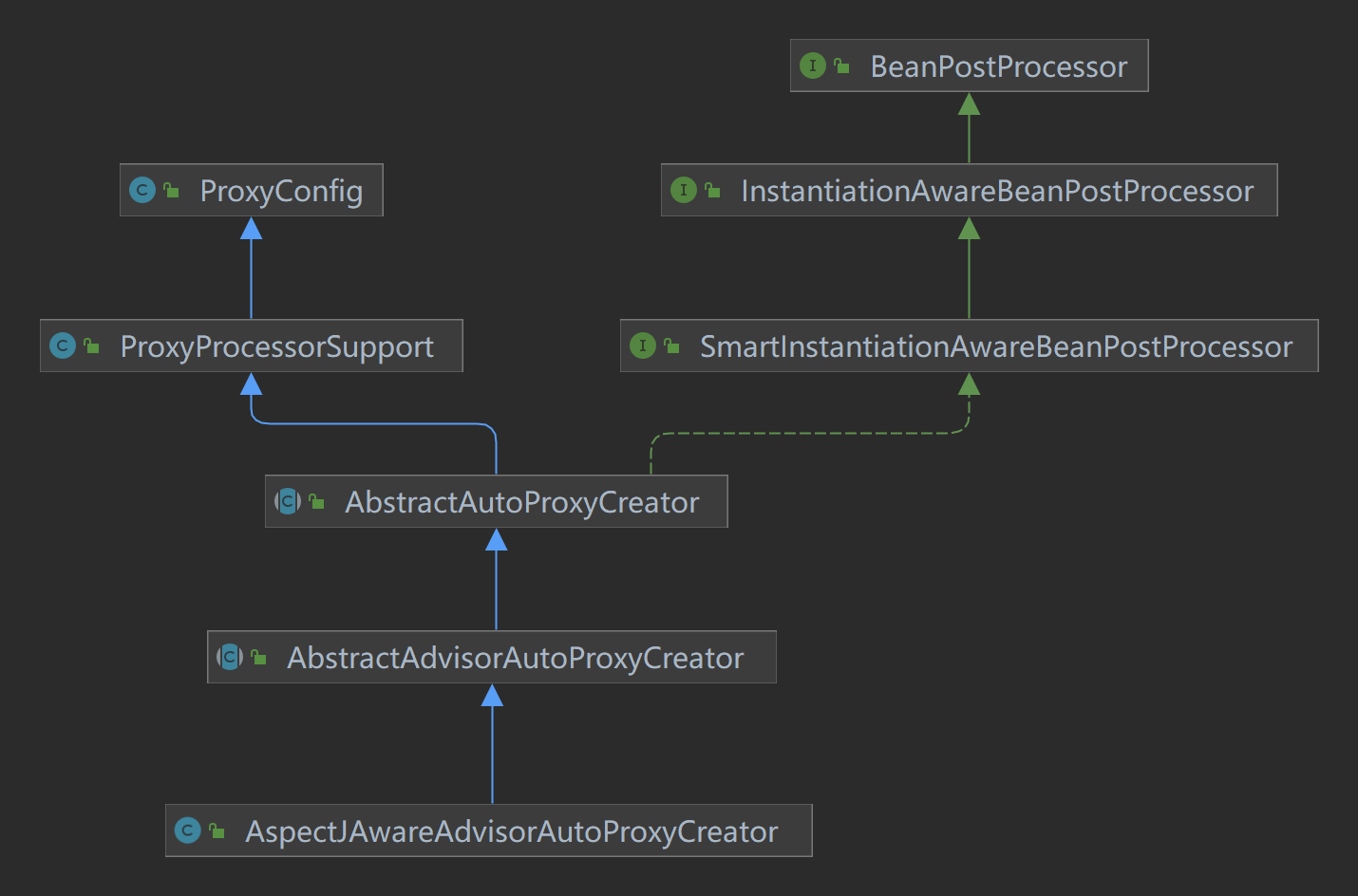
AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
定位 : org.springframework.aop.aspectj.autoproxy.AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
AbstractAutoProxyCreator getEarlyBeanReference
定位 : org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#getEarlyBeanReference
三级缓存使用到
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Override public Object getEarlyBeanReference (Object bean, String beanName) { Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName); this .earlyProxyReferences.put(cacheKey, bean); return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey); }
postProcessBeforeInstantiation
定位 : org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessBeforeInstantiation
bean 实例化之前, 对 自定义的 TargetSource 进行代理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation (Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName); if (!StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) || !this .targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { if (this .advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) { return null ; } if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) { this .advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return null ; } } TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName); if (targetSource != null ) { if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName)) { this .targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName); } Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource); Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource); this .proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } return null ; }
postProcessAfterInitialization
定位 : org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization
初始化完成后创建代理对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization (@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) { if (bean != null ) { Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName); if (this .earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) { return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey); } } return bean; }
wrapIfNecessary
定位 : org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#wrapIfNecessary
先判断是否已经处理过,是否需要跳过,跳过的话直接就放进advisedBeans里,表示不进行代理,如果这个bean处理过了,获取通知拦截器,然后开始进行代理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 protected Object wrapIfNecessary (Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) { if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this .targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { return bean; } if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this .advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) { return bean; } if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) { this .advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; } Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null ); if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { this .advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE); Object proxy = createProxy( bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource (bean)); this .proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } this .advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; }
createProxy
定位 : org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#createProxy
进行代理工厂的创建,然后判断是否需要设置 proxyTargetClass,以便于后面决定是不是要进行 jdk动态代理还是 cglib 的动态代理, 然后把通知器 advisors 包装下,加入到代理工厂,获取代理对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 protected Object createProxy (Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) { if (this .beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) { AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this .beanFactory, beanName, beanClass); } ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory (); proxyFactory.copyFrom(this ); if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) { if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) { proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true ); } else { evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory); } } Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors); proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors); proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource); customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory); proxyFactory.setFrozen(this .freezeProxy); if (advisorsPreFiltered()) { proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true ); } return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader()); } protected Advisor[] buildAdvisors(@Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors) { Advisor[] commonInterceptors = resolveInterceptorNames(); List<Object> allInterceptors = new ArrayList <>(); if (specificInterceptors != null ) { allInterceptors.addAll(Arrays.asList(specificInterceptors)); if (commonInterceptors.length > 0 ) { if (this .applyCommonInterceptorsFirst) { allInterceptors.addAll(0 , Arrays.asList(commonInterceptors)); } else { allInterceptors.addAll(Arrays.asList(commonInterceptors)); } } } if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { int nrOfCommonInterceptors = commonInterceptors.length; int nrOfSpecificInterceptors = (specificInterceptors != null ? specificInterceptors.length : 0 ); logger.trace("Creating implicit proxy for bean '" + beanName + "' with " + nrOfCommonInterceptors + " common interceptors and " + nrOfSpecificInterceptors + " specific interceptors" ); } Advisor[] advisors = new Advisor [allInterceptors.size()]; for (int i = 0 ; i < allInterceptors.size(); i++) { advisors[i] = this .advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(allInterceptors.get(i)); } return advisors; }
advisorAdapterRegistry#wrap org.springframework.aop.framework.adapter.DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry#wrap
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 @Override public Advisor wrap (Object adviceObject) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException { if (adviceObject instanceof Advisor) { return (Advisor) adviceObject; } if (!(adviceObject instanceof Advice)) { throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException (adviceObject); } Advice advice = (Advice) adviceObject; if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) { return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor (advice); } for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this .adapters) { if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) { return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor (advice); } } throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException (advice); }
ProxyProcessorSupport
定位 : org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyProcessorSupport
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 protected void evaluateProxyInterfaces (Class<?> beanClass, ProxyFactory proxyFactory) { Class<?>[] targetInterfaces = ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(beanClass, getProxyClassLoader()); boolean hasReasonableProxyInterface = false ; for (Class<?> ifc : targetInterfaces) { if (!isConfigurationCallbackInterface(ifc) && !isInternalLanguageInterface(ifc) && ifc.getMethods().length > 0 ) { hasReasonableProxyInterface = true ; break ; } } if (hasReasonableProxyInterface) { for (Class<?> ifc : targetInterfaces) { proxyFactory.addInterface(ifc); } } else { proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true ); } } protected boolean isConfigurationCallbackInterface (Class<?> ifc) { return (InitializingBean.class == ifc || DisposableBean.class == ifc || Closeable.class == ifc || AutoCloseable.class == ifc || ObjectUtils.containsElement(ifc.getInterfaces(), Aware.class)); } protected boolean isInternalLanguageInterface (Class<?> ifc) { return (ifc.getName().equals("groovy.lang.GroovyObject" ) || ifc.getName().endsWith(".cglib.proxy.Factory" ) || ifc.getName().endsWith(".bytebuddy.MockAccess" )); }
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
定位 : org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean( Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) { List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName); if (advisors.isEmpty()) { return DO_NOT_PROXY; } return advisors.toArray(); }
findEligibleAdvisors
定位 : org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#findEligibleAdvisors
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors (Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName); extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) { eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); } return eligibleAdvisors; }
extendAdvisors
定位 : org.springframework.aop.aspectj.autoproxy.AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#extendAdvisors
将 ExposeInvocationInterceptor 添加到 advice 链的开头。使用AspectJ切入点表达式时需要此附加建议,以及在使用AspectJ风格的建议时。
1 2 3 protected void extendAdvisors (List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors) { AspectJProxyUtils.makeAdvisorChainAspectJCapableIfNecessary(candidateAdvisors); }
定位 : org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJProxyUtils#makeAdvisorChainAspectJCapableIfNecessary
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public static boolean makeAdvisorChainAspectJCapableIfNecessary (List<Advisor> advisors) { if (!advisors.isEmpty()) { boolean foundAspectJAdvice = false ; for (Advisor advisor : advisors) { if (isAspectJAdvice(advisor)) { foundAspectJAdvice = true ; break ; } } if (foundAspectJAdvice && !advisors.contains(ExposeInvocationInterceptor.ADVISOR)) { advisors.add(0 , ExposeInvocationInterceptor.ADVISOR); return true ; } } return false ; }
AopUtils#findAdvisorsThatCanApply
定位 : org.springframework.aop.support.AopUtils#findAdvisorsThatCanApply
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply (List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) { if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) { return candidateAdvisors; } List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList <>(); for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty(); for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { continue ; } if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } return eligibleAdvisors; } public static boolean canApply (Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) { Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null" ); if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) { return false ; } MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher(); if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) { return true ; } IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null ; if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) { introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher; } Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet <>(); if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) { classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass)); } classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass)); for (Class<?> clazz : classes) { Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz); for (Method method : methods) { if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ? introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) : methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) { return true ; } } } return false ; }